Scope:
Setup a fully functional & authorities time service across Active Directory to ensure all AD joined Windows systems are properly time-synced to the domain controller(s) and also to external sources when abroad.
The Primary Domain Controller:
In Active Directory, the PDC Emulator should get the time from an external time source and then all member computers of this domain will get the correct time from the PDC. Since the PDC Emulator can move around, we make sure the GPO is applied only to the current PDC Emulator using a WMI filter.
Go to the WMI Filters section in GPMC and create a new filter like the following:
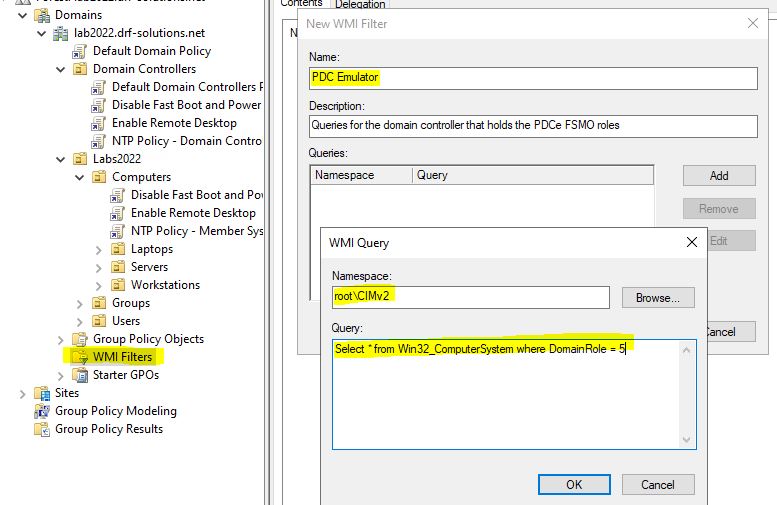
Here’s the query for you to copy’n’paste:
Select * from Win32_ComputerSystem where DomainRole = 5
Create a GPO called NTP Policy – PDC and apply it to the Domain Controllers OU
Apply the WMI filter you created earlier
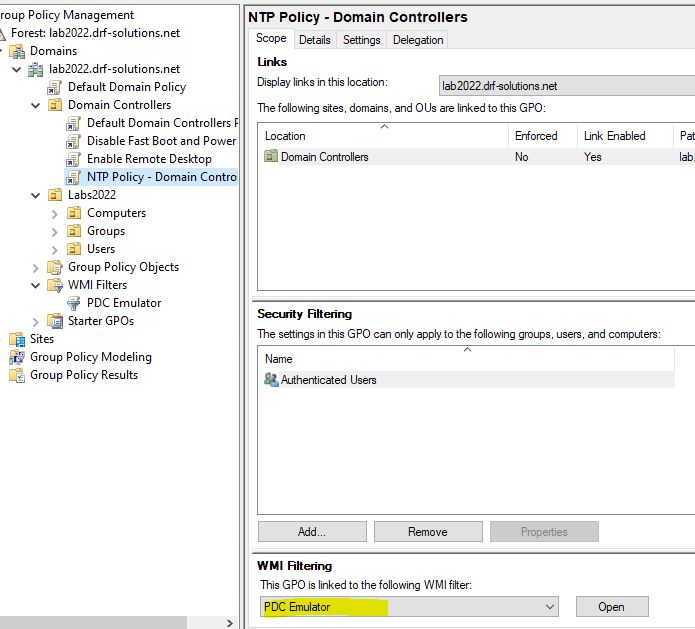
Drill down into:
Computer Configuration/Policies/Administrative Templates/System/Windows Time Service/Time Providers
Edit all three policy items in this folder:
Next, we need to allow the NTP requests to hit the domain controller, so drill down into:
Computer Configuration\Policies\Windows Settings\Security Policies\Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security\Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security\Inbound Rules
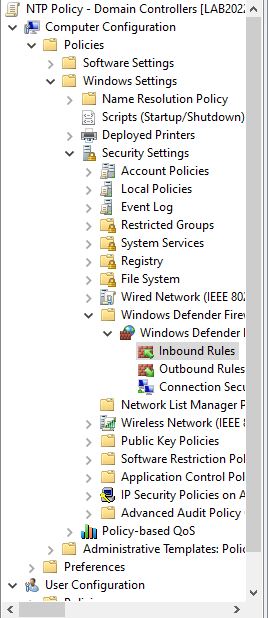
Right-click on the Inbound Rules tree item and select New Rule…
Choose Port and click Next
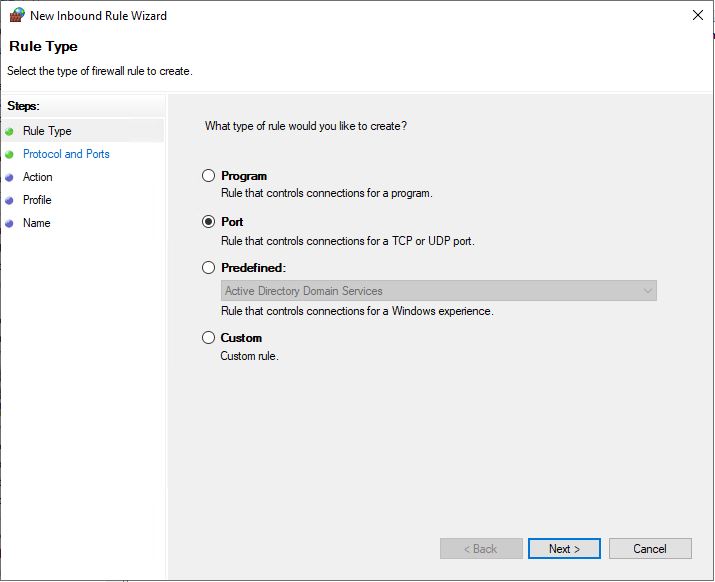
Select UDP and specify port 23. Click Next
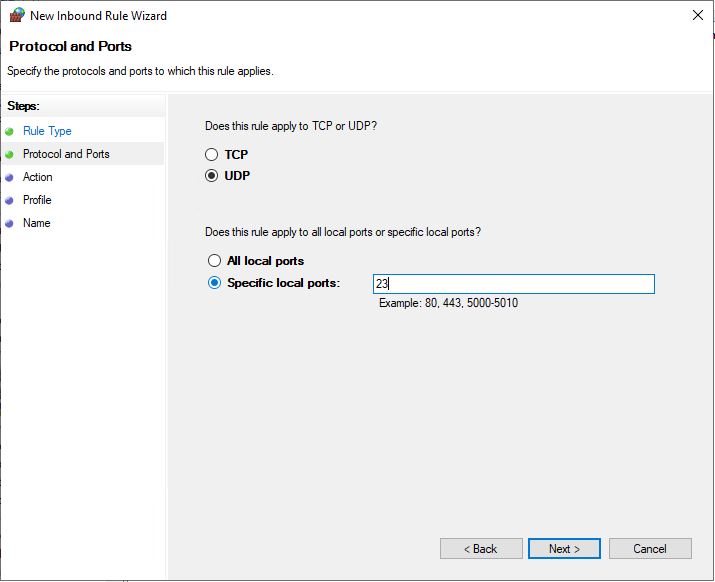
Select Allow the connection and click Next
Ensure all network profiles are selected and click Next
Give the rule a name, such as NTP-in and click Finish
The final result will look something like this:

Additional Domain Controllers:
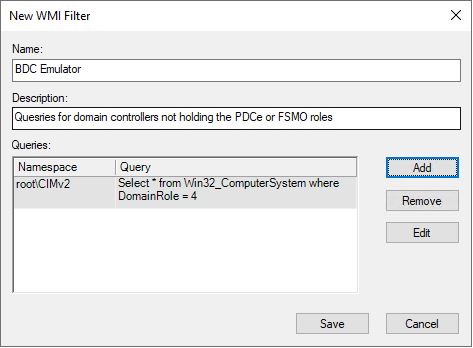
Now we need to create another WMI Filter called BDC Emulator and use the following query:
Select * from Win32_ComputerSystem where DomainRole = 4
Create a new GPO in the Domain Controllers OU called NTP Policy – BDC
Link the WMI Filter for BDC Emulator
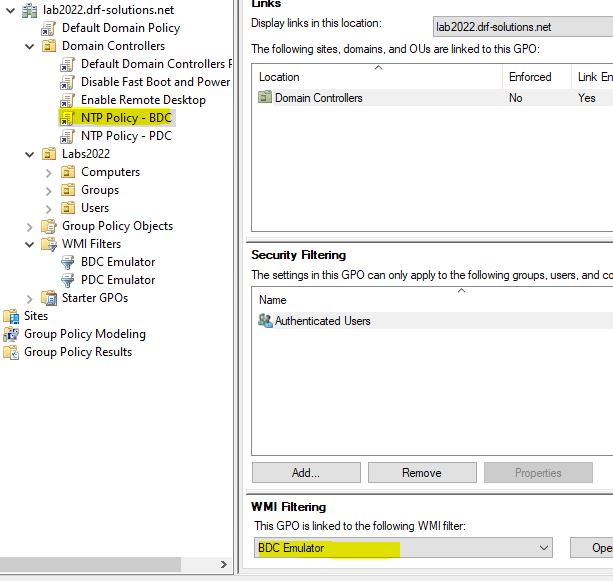
Now edit this GPO and drill down to:
Computer Configuration/Policies/Administrative Templates/System/Windows Time Service/Time Providers
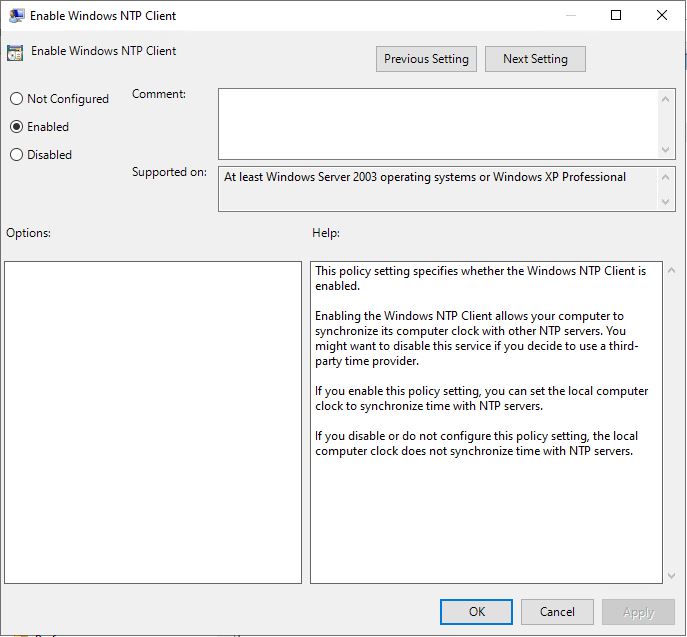
Double-click Enable Windows NTP Client
Set to Enabled and click OK

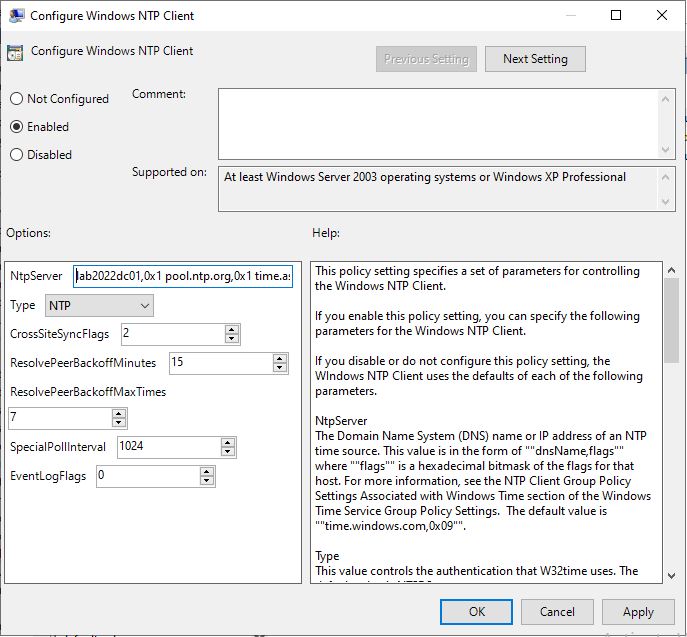
Double-click on Configure Windows NTP Client
Set Type to NTP
Set NtpServer to hold the PDC and also a couple of external time providers that match what you specified in the PDC GPO
Click OK and close that policy
Congratulations! You have configured the NTP GPOs for the domain controllers.
Now we need to configure NTP for the rest of the domain members
Configure NTP for Domain Member Systems:
Finally, create a new GPO and link it to the OU where member servers, laptops, and workstations reside
Call it something like NTP Policy – Member Systems
Again, drill down to:
Computer Configuration/Policies/Administrative Templates/System/Windows Time Service/Time Providers
Double-click Enable Windows NTP Client
Set to Enabled and click OK

Double-click on Configure Windows NTP Client
Set Type to NTP
Set NtpServer to hold the PDC and also a couple of external time providers that match what you specified in the PDC GPO

Click OK and close that policy
Congratulations! You should now have successfully configured full AD NTP sync across the network.
Perform a gpupdate on systems to ensure policies are applying, use gpresult to ensure the policies are being read & applied.
In some cases, you may need to restart the Windows Time Service or reboot systems.
NTP GPO details explained
So what all these settings mean.
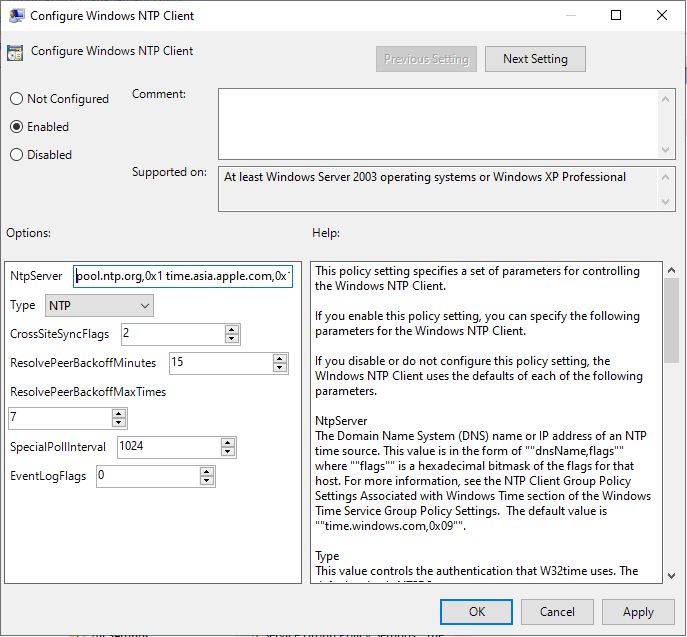
Configuring Windows NTP Client: Enabled
NtpServer:
- Here you specify which NtpServers to use separated by a space but also with a special NTP flag. I decided to use the public ntp.org pools:
0.se.pool.ntp.org,0x1 1.se.pool.ntp.org,0x1 2.se.pool.ntp.org,0x1 3.se.pool.ntp.org,0x1
The NtpFlags are explained in detail here but 0x1 means: “Instead of following the NTP specification, wait for the interval specified in the SpecialPollInterval entry before attempting to recontact this time source. Setting this flag decreases network usage, but it also decreases accuracy.” where SpecialPollInterval is specified in the GPO (in our, case 3600 seconds)
- The rest of the settings are explained in the GPO Help.
Enable Windows NTP Client: Enabled
- Is a must, otherwise the computer will not sync with other NTP serves since it’s disabled by default.
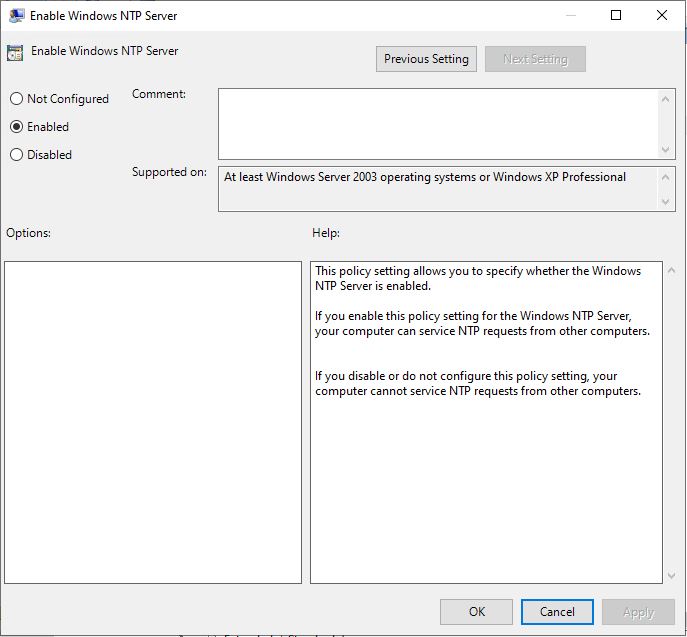
Enable Windows NTP Server: Enabled
- Is a must, otherwise the computer will not allow other computers to sync with it since it’s disabled by default.
Where is the configuration stored?
First, never edit the registry for NTP. If something is not working, clear the configuration and start from scratch and configure NTP using GPO or W32tm.exe. Do this by running the following commands:
Stop-Service w32time
w32tm /unregister
w32tm /register
Start-Service w32time
Still, you might want to check where the configuration is. When using GPO, the configuration is stored here:
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\W32Time\Parameters
Note that this is different if you’re using w32tm.exe, then the configuration is stored here:
HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\W32Time\Parameters
Useful tools when troubleshooting NTP
W32tm is still your friend and here are my favorites:
w32tm.exe /resync /rediscover /nowait
Resynchronize the clock as soon as possible, disregarding all accumulated error statistics. It will not wait for resynchronization and will force redetection of sources.
w32tm /query /peers
Displays all configured peers you have configured
w32tm /query /source
Displays the currently used time source. Note that after a restart of the service, it might show Local CMOS Clock until everything has refreshed properly.
w32tm /query /status
Displays the current status
w32tm /query /configuration
Displays the configuration
w32tm /debug /enable /file:C:\Temp\w32tmdebug.log /size:10485760 /entries:0-300
If you really want to get dirty, enable the debug log
Troubleshooting
Many things can go wrong when configuring NTP. Here are some suggestions:
- Don’t forget to allow NTP traffic (udp/123) in your firewall(s) – if you have 3rd party firewalls, check them also
- Enable the debug log and check that the service actually tries to communicate with the NTP serves. You can lower the SpecialPollInterval to 30 seconds to speed up your troubleshooting.
- Restart the service and maybe even the server, sometimes this has solved it.
- Also monitor the event log since the service logs there too.
- If the domain controller is a Hyper-V VM, disable Time Synchronization on the guest
Attachments
This attachment is a client script that can be used to force reconfiguration of the local sync setup of workstations and member servers…
clocksyncupdate.cmd